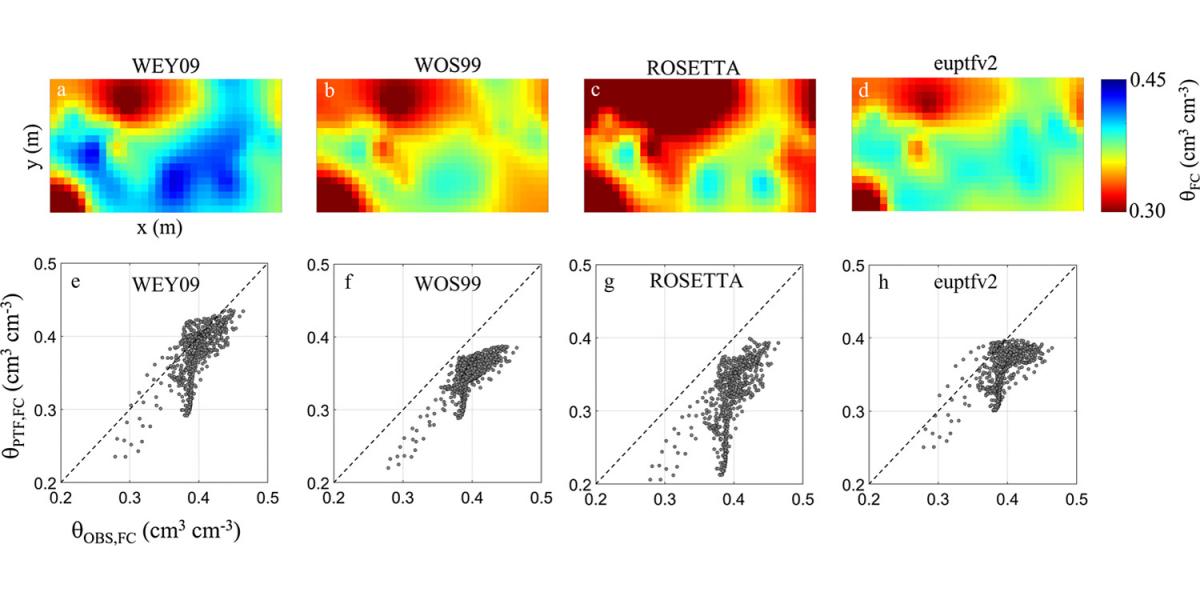
In collaboration with the researchers of the University of Naples Federico II, our senior scientist Brigitta Szabó analysed the efficiency of European hydraulic pedotransfer functions (PTFs) available from the literature. The parametric evaluation of eleven PTFs to predict the water retention function and ten PTFs to predict the saturated hydraulic conductivity was performed on relatively large, three Eruropean soil hydraulic datasets. The best performing PTFs were applied to map filed capacity of an Italian case study site and used the PTF-predicted soil hydraulic properties for soil profile scale water flux simulation. The euptfv2, Weynants and Wösten PTFs proved to be accurate enough for predicting the water retention function. The ten PTFs used to predict saturated hydraulic had uncertainty spanning over one or two orders of magnitude, which – among other reasons – might be due to the lack of its standardized measurement method. In the preparation of field capacity maps euptfv2 and Weynants PTF performed the best, having the lowest root mean squared error. During the simulation the most accurate predictions were provided by euptfv2 for field capacity and Weynants PTF for saturated conductivity. Although the four PTFs proved satisfactorily equivalent for simulating daily water storage values, it has to be stressed that the importance of describing the sensitivity of model output to model parameterization.
The results of this research was published in the Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, which is a highly ranked journal in the field of Water Science and Technology (D1).
Further information:
Nasta, P., Szabó, B. & Romano, N. 2021. Evaluation of pedotransfer functions for predicting soil hydraulic properties : A voyage from regional to field scales across Europe. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 37, 100903.